🌍 Earth, Moon and The Sun
Class 7, Tap each question to show or hide the answer
🌞 Q1. How do day and night occur on the Earth due to its rotation?
💬 Answer:
Day and night occur because the Earth rotates from west to east 🌍.
The side of the Earth that faces the Sun has daytime 🌞, while the side that is turned away from the Sun has night 🌙.
The side of the Earth that faces the Sun has daytime 🌞, while the side that is turned away from the Sun has night 🌙.
✨ Did you know?
Earth completes one full rotation in about 24 hours,
which gives us one day and one night.
🌟 Q2. Since the Earth is rotating, shouldn’t the stars also appear to move in the sky like the Sun?
💬 Answer:
Yes, they do appear to move. Because the Earth is rotating, the stars seem to move across
the sky from east to west ✨➡️.
This movement is only apparent – it happens because we (on Earth) are spinning on the Earth’s axis, not because the stars are actually moving around us.
This movement is only apparent – it happens because we (on Earth) are spinning on the Earth’s axis, not because the stars are actually moving around us.
✨ Did you know?
The Pole Star looks almost fixed in the sky because it lies nearly along the
axis of rotation of the Earth.
🌌 Q3. Why do different stars appear in the night sky over the course of a year?
💬 Answer:
Different stars appear in the night sky across the year because the Earth
revolves around the Sun 🌞🌍.
As the Earth moves along its orbit, we look at different directions in space at night, so new groups of stars and constellations become visible in different months.
As the Earth moves along its orbit, we look at different directions in space at night, so new groups of stars and constellations become visible in different months.
✨ Did you know?
Orion is a famous winter constellation, best seen in the sky
around December and January.
🍂 Q4. We go through a cycle of seasons every year. Is it related to the revolution of the Earth around the Sun?
💬 Answer:
Yes. Seasons occur because the Earth’s axis is tilted and the Earth
revolves around the Sun ❄️☀️🍁🌸.
Due to this tilt, different parts of the Earth receive different amounts of sunlight at different times of the year, which causes the change of seasons.
Due to this tilt, different parts of the Earth receive different amounts of sunlight at different times of the year, which causes the change of seasons.
✨ Did you know?
If the Earth’s axis were not tilted, we would hardly have any seasons –
the climate in most places would stay almost the same throughout the year.
⏱️ Q5. Why are days longer in summer than in winter?
💬 Answer:
Days are longer in summer because your part of the Earth is
tilted towards the Sun ☀️⏳.
As a result, the Sun stays above the horizon for more hours each day, so you get a longer daytime and a shorter night.
As a result, the Sun stays above the horizon for more hours each day, so you get a longer daytime and a shorter night.
✨ Did you know?
Near the poles, the Sun may not set at all for many days in summer.
This amazing phenomenon is called the “Midnight Sun”.
🌞 Q6. Could the light from the Sun get blocked by the two planets that revolve between the Earth and the Sun?
💬 Answer:
No. The two planets between the Earth and the Sun are Mercury and Venus.
They are much smaller than the Sun and are also very far from us 🌞.
Even when they come between the Earth and the Sun, they block only a tiny portion of the Sun’s light, so we do not experience a complete blocking of sunlight.
Even when they come between the Earth and the Sun, they block only a tiny portion of the Sun’s light, so we do not experience a complete blocking of sunlight.
✨ Did you know?
When Mercury or Venus passes directly in front of the Sun as seen from Earth,
the event is called a transit. The planet looks like a small dark dot moving across the Sun’s disc.
📘 NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science – Chapter 12
Earth, Moon and the Sun
📝 Questions, Answers & Explanations
✨ Let Us Enhance Our Learning
🌞 Q1. In the diagram, how many hours of sunlight do the North Pole and South Pole receive during one rotation of the Earth?
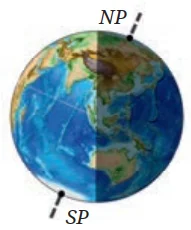
📷 Sunlight on the North Pole and South Pole during one full rotation of Earth
💬 Answer:
• North Pole: 🌞 24 hours of sunlight
• South Pole: 🌑 0 hours (complete darkness)
• South Pole: 🌑 0 hours (complete darkness)
📚 Explanation:
In June, the North Pole is tilted towards the Sun,
so it receives sunlight for the entire 24 hours.
The South Pole is tilted away from the Sun, so it stays in darkness for 24 hours.
The South Pole is tilted away from the Sun, so it stays in darkness for 24 hours.
✏️ Q2. Fill in the blanks
(i) Stars rise in the _________ and set in the ___________.
(ii) Day and night are caused by the Earth’s __________________.
(iii) When the Moon fully covers the Sun from our view, it is called a _____________ solar eclipse.
(ii) Day and night are caused by the Earth’s __________________.
(iii) When the Moon fully covers the Sun from our view, it is called a _____________ solar eclipse.
💬 Answer:
(i) Stars rise in the East and set in the West. 🌟
(ii) Day and night are caused by the Earth’s rotation. 🌍
(iii) When the Moon fully covers the Sun from our view, it is called a total solar eclipse. 🌑☀️
(ii) Day and night are caused by the Earth’s rotation. 🌍
(iii) When the Moon fully covers the Sun from our view, it is called a total solar eclipse. 🌑☀️
📚 Explanation:
• Earth rotates from west to east, so stars and the Sun appear to move from east to west in the sky.
• The rotation of Earth creates day and night.
• A total solar eclipse happens when the Moon blocks the entire disc of the Sun.
• The rotation of Earth creates day and night.
• A total solar eclipse happens when the Moon blocks the entire disc of the Sun.
✅ Q3. State whether the following statements are True or False
💬 Answers:
(i) Lunar eclipse occurs when the Sun comes between the Earth and the Moon.
— ❌ False
➡️ Lunar eclipse happens when Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon.
(ii) Sunrise happens earlier in Gujarat than in Jharkhand. — ❌ False
➡️ Jharkhand lies more to the east, so sunrise happens earlier there.
(iii) In Chennai, the longest day occurs on the summer solstice. — ✔️ True
➡️ The summer solstice in June gives the longest daytime for all places in the Northern Hemisphere.
(iv) We should watch the solar eclipse directly with our naked eye. — ❌ False
➡️ It is dangerous and can damage our eyes.
(v) Seasons occur due to the tilt of Earth’s axis of rotation and its spherical shape. — ✔️ True
➡️ The tilt of Earth’s axis and its spherical shape cause unequal heating → seasons.
(vi) The Earth’s revolution around the Sun causes day and night. — ❌ False
➡️ Rotation of Earth causes day and night, not revolution.
➡️ Lunar eclipse happens when Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon.
(ii) Sunrise happens earlier in Gujarat than in Jharkhand. — ❌ False
➡️ Jharkhand lies more to the east, so sunrise happens earlier there.
(iii) In Chennai, the longest day occurs on the summer solstice. — ✔️ True
➡️ The summer solstice in June gives the longest daytime for all places in the Northern Hemisphere.
(iv) We should watch the solar eclipse directly with our naked eye. — ❌ False
➡️ It is dangerous and can damage our eyes.
(v) Seasons occur due to the tilt of Earth’s axis of rotation and its spherical shape. — ✔️ True
➡️ The tilt of Earth’s axis and its spherical shape cause unequal heating → seasons.
(vi) The Earth’s revolution around the Sun causes day and night. — ❌ False
➡️ Rotation of Earth causes day and night, not revolution.
🌟 Q4. Padmashree saw the Orion constellation overhead at 8 pm yesterday. When will she see Orion overhead today?
💬 Answer:
🌟 She will see Orion overhead at about 7:56 pm (around 4 minutes earlier than the previous day).
📚 Explanation:
Because of Earth’s revolution around the Sun, star patterns appear
about 4 minutes earlier each night in the sky.
✨ Q5. Nandhini saw a group of stars rising at midnight on 21 June. When will she see the same group rising at midnight next year?
💬 Answer:
📅 She will see the same group of stars rising at midnight again around 21 June next year.
📚 Explanation:
Star positions in the sky repeat every one year
because Earth completes one full revolution around the Sun.
🌍 Q6. Why was it daytime in India while it was night-time in the USA for Abhay’s uncle?
💬 Answer:
🌍 Because Earth rotates, different parts of it face the Sun at different times.
📚 Explanation:
• When India faces the Sun, it has daytime.
• The USA is then facing away from the Sun, so it has night-time.
Earth’s rotation creates different time zones on the globe.
• The USA is then facing away from the Sun, so it has night-time.
Earth’s rotation creates different time zones on the globe.
😎 Q7. Four friends used the following ways to see the solar eclipse. Who among them was being careless?
(i) Ravikiran used a solar eclipse goggle.
(ii) Jyothi used a mirror to project the Sun’s image.
(iii) Adithya saw the Sun directly with his eyes.
(iv) Aruna attended a programme arranged by a planetarium.
(ii) Jyothi used a mirror to project the Sun’s image.
(iii) Adithya saw the Sun directly with his eyes.
(iv) Aruna attended a programme arranged by a planetarium.
💬 Answer:
😬 Adithya was being careless.
📚 Explanation:
He looked at the Sun directly, which is very dangerous and can damage the eyes.
The others used safe methods like eclipse goggles, projection, or a planetarium programme.
The others used safe methods like eclipse goggles, projection, or a planetarium programme.
🌑 Q8. Fill in the circles in the diagram appropriately with one of the following: Sun, Moon, Earth.
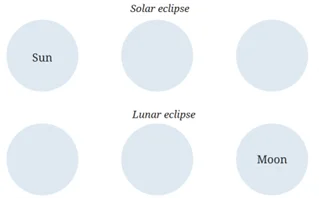
📷 Diagram for solar and lunar eclipse – fill the circles with Sun, Moon, and Earth
💬 Answer:
Solar eclipse (top row):
Left → Sun
Middle → Moon
Right → Earth
Lunar eclipse (bottom row):
Left → Sun
Middle → Earth
Right → Moon
Left → Sun
Middle → Moon
Right → Earth
Lunar eclipse (bottom row):
Left → Sun
Middle → Earth
Right → Moon
📚 Explanation:
• In a solar eclipse, the Moon comes between the Sun and the Earth and blocks the Sun.
• In a lunar eclipse, the Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon and blocks sunlight from reaching the Moon.
• In a lunar eclipse, the Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon and blocks sunlight from reaching the Moon.
🌙 Q9. The Moon is much smaller than the Sun, yet it can block the Sun completely from our view during a total solar eclipse. Why is it possible?
💬 Answer:
🌙➡️☀️ It is possible because the Moon is much closer to Earth,
so it appears almost the same size as the Sun in the sky.
📚 Explanation:
• The Sun is very large, but it is also very far away from Earth.
• The Moon is much smaller, but it is much closer to Earth.
Because of this, their apparent sizes in the sky look similar, so the Moon can cover the Sun completely during a total solar eclipse.
• The Moon is much smaller, but it is much closer to Earth.
Because of this, their apparent sizes in the sky look similar, so the Moon can cover the Sun completely during a total solar eclipse.
🏏 Q10. The Indian cricket team matches in Australia are often held in December. Should they pack winter or summer clothes for their trip?
💬 Answer:
☀️ They should pack summer clothes.
📚 Explanation:
• December is winter in India (Northern Hemisphere).
• But in the Southern Hemisphere (including Australia), December is summer.
So the Indian team will experience summer weather in Australia.
• But in the Southern Hemisphere (including Australia), December is summer.
So the Indian team will experience summer weather in Australia.
🌕 Q11. Why can lunar eclipses be seen from a large part of the Earth, but total solar eclipses can be seen only from a small part?
💬 Answer:
🌕 Because Earth’s shadow is very large, but the Moon’s shadow is very small.
📚 Explanation:
• During a lunar eclipse, Earth’s big shadow covers the entire Moon,
so people in a large part of the world can see it.
• During a total solar eclipse, only the tiny central shadow of the Moon falls on Earth. This small region is where people can see the total eclipse, so it is visible to only a small area.
• During a total solar eclipse, only the tiny central shadow of the Moon falls on Earth. This small region is where people can see the total eclipse, so it is visible to only a small area.
🌍 Q12. If the Earth’s axis were not tilted with respect to the axis of revolution, what would be the effect on seasons?
💬 Answer:
🌍 There would be no seasons – the weather would remain almost the same throughout the year.
📚 Explanation:
• With no tilt, the Sun’s rays would fall almost equally on each place throughout the year.
• Each place would have nearly equal day and night every day.
So there would be no clear summer or winter, and hardly any seasonal changes.
• Each place would have nearly equal day and night every day.
So there would be no clear summer or winter, and hardly any seasonal changes.
