🐄 Q1. According to you, whose statement is correct and why? (Page No. 215)
📜 Statement 1: The cow is standing in the Sun. But it does not mean that it is getting energy from the Sun.
📜 Statement 2: The cow is eating grass. Grass leaves need sunlight to grow. So, the main source of energy is the Sun. This way the cow gets energy from the Sun.
📜 Statement 2: The cow is eating grass. Grass leaves need sunlight to grow. So, the main source of energy is the Sun. This way the cow gets energy from the Sun.
💬 Answer:
👉 Statement 2 is correct. 🌞
🐄 A cow gets energy from the grass it eats, and the grass makes its food using sunlight through photosynthesis. 🌿
So, the cow indirectly gets energy from the Sun by eating plants that store solar energy as food. ☀️➡️🌿➡️🐄
🐄 A cow gets energy from the grass it eats, and the grass makes its food using sunlight through photosynthesis. 🌿
So, the cow indirectly gets energy from the Sun by eating plants that store solar energy as food. ☀️➡️🌿➡️🐄
💡 Did You Know?
All living beings — even humans — get their energy from the Sun, either directly (plants) or indirectly (animals that eat plants)! 🌞🍃
Q2.❓ What will happen if the Sun is not visible for a few days? (Page No. 216)
1️⃣ We may have to depend on artificial lighting during daytime also.
2️⃣ _______________
3️⃣ _______________
2️⃣ _______________
3️⃣ _______________
💬 Answer:
1️⃣ We may have to depend on artificial lighting during daytime also. 💡
2️⃣ Plants will not be able to make food through photosynthesis because they need sunlight to prepare their food. 🌿
3️⃣ The weather will become very cold, and animals and humans may find it difficult to survive due to lack of warmth. ❄️
2️⃣ Plants will not be able to make food through photosynthesis because they need sunlight to prepare their food. 🌿
3️⃣ The weather will become very cold, and animals and humans may find it difficult to survive due to lack of warmth. ❄️
💡 Did You Know?
The Sun is the ultimate source of energy for all living things — it gives us light, heat, and life! 🌞🌍
🌲 Q3.❓ What are the consequences of cutting a large forest area? (Page No. 217)
💬 Answer (Explanation):
Cutting down large forest areas is called deforestation. It has many harmful effects:
1️⃣ Loss of habitats for animals 🐘🦜
2️⃣ Increase in carbon dioxide and decrease in oxygen 🌫️
3️⃣ Soil erosion and floods due to lack of tree roots 🌧️
4️⃣ Less rainfall and hotter climate ☀️
5️⃣ Loss of biodiversity — plants and animals may die or disappear ⚠️
1️⃣ Loss of habitats for animals 🐘🦜
2️⃣ Increase in carbon dioxide and decrease in oxygen 🌫️
3️⃣ Soil erosion and floods due to lack of tree roots 🌧️
4️⃣ Less rainfall and hotter climate ☀️
5️⃣ Loss of biodiversity — plants and animals may die or disappear ⚠️

💡 Did You Know?
Forests are called the “lungs of the Earth” — they breathe in carbon dioxide and breathe out oxygen, keeping our planet alive! 🌎🌳
🤔 Let us enhance our learning 📌
🌏 Q.1. Given diagram shows items related to natural resources. Match them with their jumbled-up names. Make another table and write the names of these resources. Classify these resources as renewable or non-renewable.

(Match them with their jumbled up names)
💬 Answer:

(the names of these resources)
| Resource | Category |
|---|---|
| Water 💧 | Renewable resource ♻️ |
| Wind 💨 | Renewable resource ♻️ |
| Forest 🌳 | Renewable resource ♻️ |
| Rock 🪨 | Non-renewable resource ⛏️ |
✅ Explanation:
🌊 Water and 💨 Wind can be naturally replenished → Renewable.
🌳 Forest regrows through natural processes → Renewable.
🪨 Rock takes millions of years to form → Non-renewable.
🌊 Water and 💨 Wind can be naturally replenished → Renewable.
🌳 Forest regrows through natural processes → Renewable.
🪨 Rock takes millions of years to form → Non-renewable.
🌿 Q2. ❓ State whether the following statements are True [T] or False [F].
If False, correct them.
💬 Answer:
(i) ✅ True — Nature provides air, water, sunlight, soil, and minerals that fulfill our basic needs. 🌏
(ii) ❌ False — Machines are man-made resources, created using natural materials. ⚙️
(iii) ✅ True — Natural gas is a non-renewable resource. It cannot be replaced quickly once used; it takes millions of years to form. ⛽
(iv) ✅ True — Air is a renewable resource. It is naturally available and keeps getting renewed through the atmosphere. 💨
(ii) ❌ False — Machines are man-made resources, created using natural materials. ⚙️
(iii) ✅ True — Natural gas is a non-renewable resource. It cannot be replaced quickly once used; it takes millions of years to form. ⛽
(iv) ✅ True — Air is a renewable resource. It is naturally available and keeps getting renewed through the atmosphere. 💨
💡 Did You Know?
Resources like sunlight, wind, and water never run out — but coal, oil, and natural gas might, if we don’t use them wisely! 🌞💨🌊
⚡ Q.3. Fill in the blanks using the most appropriate option —
(i) A fuel that is commonly used in two-wheelers like scooters or bikes is ___________.
(a) Kerosene
(b) Petrol
(c) Diesel
(d) LPG
(a) Kerosene
(b) Petrol
(c) Diesel
(d) LPG
✅ Answer: (b) Petrol ⛽
💡 Explanation: Two-wheelers run mainly on petrol engines, which burn fuel to produce energy for movement. 🛵
💡 Explanation: Two-wheelers run mainly on petrol engines, which burn fuel to produce energy for movement. 🛵
(ii) An example of a renewable resource is ___________.
(a) Coal
(b) Water
(c) Natural gas
(d) Petrol
(a) Coal
(b) Water
(c) Natural gas
(d) Petrol
✅ Answer: (b) Water 💧
💡 Explanation: Water is a renewable resource because it keeps recycling naturally through the water cycle — evaporation, condensation, and rainfall. 🌦️
💡 Explanation: Water is a renewable resource because it keeps recycling naturally through the water cycle — evaporation, condensation, and rainfall. 🌦️
💡 Did You Know?
Unlike coal and petrol, renewable resources like sunlight, air, and water never get exhausted — they’re Earth’s endless gifts! 🌍☀️💨
🌿 Q.4. Classify the following as renewable or non-renewable resources — coal, natural gas, forests, and minerals.
💬 Answer:
• Renewable resources: Forests 🌳
• Non-renewable resources: Coal ⛏️, Natural gas ⛽, Minerals 💎
• Non-renewable resources: Coal ⛏️, Natural gas ⛽, Minerals 💎
💡 Explanation: Renewable resources like forests can grow again over time, but coal, natural gas, and minerals take millions of years to form — once used, they’re gone for a long time. ⏳
⛽ Q.5. Why do we say that petroleum is a non-renewable resource?
💬 Answer:
Petroleum is a non-renewable resource because it takes millions of years to form deep under the Earth’s surface. 🌍
We are using it much faster than nature can produce it. Once exhausted, it cannot be replaced easily.
We are using it much faster than nature can produce it. Once exhausted, it cannot be replaced easily.
💡 Did You Know?
Petroleum is also called “black gold” because it’s precious and used in fuels, plastics, and many products. 🛢️💰
🌲 Q.6. It is difficult to regrow forests. Justify this statement.
💬 Answer:
Regrowing forests takes a very long time because:
1️⃣ Trees need years to grow fully. 🌳
2️⃣ Many animals lose homes, making the ecosystem weak. 🐿️
3️⃣ The soil becomes poor due to erosion after trees are cut. 🌧️
Hence, restoring a forest takes decades — which is why it’s better to protect existing forests. 🌿
1️⃣ Trees need years to grow fully. 🌳
2️⃣ Many animals lose homes, making the ecosystem weak. 🐿️
3️⃣ The soil becomes poor due to erosion after trees are cut. 🌧️
Hence, restoring a forest takes decades — which is why it’s better to protect existing forests. 🌿
💡 Did You Know?
It can take over 50–100 years for a destroyed forest to return to its original condition! ⏳🌳
💧 Q.7. Make a list of five daily activities in which you use natural resources. Suggest ways by which you can reduce their use.
💬 Answer:
| Daily Activity | Natural Resource Used | Way to Reduce Use |
|---|---|---|
| Bathing 🚿 | Water 💧 | Take shorter showers |
| Travelling 🚴 | Petrol ⛽ | Use bicycles or share rides |
| Using lights 💡 | Electricity ⚡ | Switch off lights when not needed |
| Writing ✍️ | Paper 📖 | Use both sides of paper |
| Cooking 🍲 | LPG 🔥 | Cook on medium flame and cover pots |
💡 Did You Know?
Small steps taken daily can save thousands of litres of water and kilowatts of energy each year! 🌍💪
🌬️ Q.8. List four activities that are possible due to the presence of air.
💬 Answer:
1️⃣ Breathing — Air gives oxygen for living beings to survive. 🫁
2️⃣ Flying kites or airplanes — Air helps in lift and movement. 🪁✈️
3️⃣ Burning of fuels — Needs oxygen from air to produce heat. 🔥
4️⃣ Winnowing — Air separates lighter husk from heavier grains. 🌾💨
2️⃣ Flying kites or airplanes — Air helps in lift and movement. 🪁✈️
3️⃣ Burning of fuels — Needs oxygen from air to produce heat. 🔥
4️⃣ Winnowing — Air separates lighter husk from heavier grains. 🌾💨
💡 Did You Know?
Air contains 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and a small amount of carbon dioxide and other gases! 🌍💨
🌱 Q.9. How can you contribute towards enhancing the green cover of your locality? Make a list of actions to be taken.
💬 Answer:
1️⃣ Plant trees in parks, roadsides, and school campuses. 🌳
2️⃣ Avoid wasting paper — it reduces the need to cut trees. 📚
3️⃣ Join local tree-planting drives or start one with friends. 🤝
4️⃣ Water and protect young plants regularly. 💧
5️⃣ Spread awareness about the importance of greenery. 📢
2️⃣ Avoid wasting paper — it reduces the need to cut trees. 📚
3️⃣ Join local tree-planting drives or start one with friends. 🤝
4️⃣ Water and protect young plants regularly. 💧
5️⃣ Spread awareness about the importance of greenery. 📢
💡 Did You Know?
Planting even one tree every month can make a big difference — trees cool the air, attract rain, and keep the planet alive! 🌦️💚
🍛 Q.10. In the given illustration, we see that food is being cooked.
Answer the following questions —
(i) What type of energy is being used for cooking?
(ii) Name one benefit and one drawback of using this type of energy for cooking.
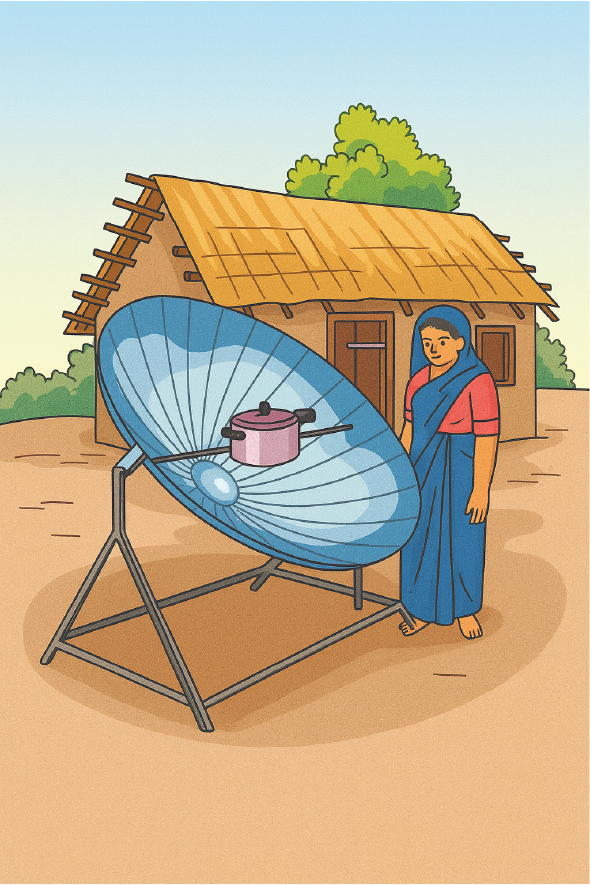

☀️ Solar cooker using sunlight to cook food.
💬 Answer:
(i) The type of energy being used for cooking is solar energy. ☀️🍲
(ii) Benefit: Solar energy is renewable and free of cost. It does not cause pollution and helps save fuels like LPG or wood. 🌿
Drawback: It cannot be used on cloudy or rainy days, and cooking takes more time than using regular stoves. ⛅⏳
(ii) Benefit: Solar energy is renewable and free of cost. It does not cause pollution and helps save fuels like LPG or wood. 🌿
Drawback: It cannot be used on cloudy or rainy days, and cooking takes more time than using regular stoves. ⛅⏳
💡 Did You Know?
A solar cooker uses mirrors to focus sunlight and convert it into heat energy — enough to boil water, cook rice, or even bake biscuits! 🍪☀️
🌲 Q.11. Cutting down trees on a large scale impacts the quality of the soil. Why do you think it is so? 🌍
💬 Answer:
When trees are cut down, their roots no longer hold the soil firmly. 🌿
As a result, rainwater washes away the top layer of soil, which contains nutrients needed for plant growth. 🌧️
This process is called soil erosion.
Over time, the soil becomes poor in quality, less fertile, and unable to support healthy vegetation. 🌾
As a result, rainwater washes away the top layer of soil, which contains nutrients needed for plant growth. 🌧️
This process is called soil erosion.
Over time, the soil becomes poor in quality, less fertile, and unable to support healthy vegetation. 🌾
💡 Did You Know?
Tree roots act like natural anchors — they hold the soil in place and help recharge groundwater. 🌳💧
💨 Q.12. Explain two ways in which human activities pollute the air. Propose one action which can help in reducing air pollution. 🌫️
💬 Answer:
🌆 Two Ways Humans Pollute the Air:
1️⃣ Smoke from Vehicles: Cars, buses, and trucks release harmful gases like carbon monoxide and smoke, which pollute the air and cause breathing problems. 🚗💨
2️⃣ Burning of Fuels and Waste: Factories and households burn coal, wood, and garbage, releasing toxic gases and soot into the air. 🏭🔥
1️⃣ Smoke from Vehicles: Cars, buses, and trucks release harmful gases like carbon monoxide and smoke, which pollute the air and cause breathing problems. 🚗💨
2️⃣ Burning of Fuels and Waste: Factories and households burn coal, wood, and garbage, releasing toxic gases and soot into the air. 🏭🔥
🌿 One Action to Reduce Air Pollution:
Plant more trees and protect green areas. 🌳
Trees absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, helping to clean the air naturally.
Plant more trees and protect green areas. 🌳
Trees absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, helping to clean the air naturally.
💡 Did You Know?
One big tree can remove over 20 kilograms of dust and pollutants from the air every year! 🌲✨
🌞 Q.13. A family uses solar panels to generate electricity, a gas stove to cook food, and a windmill for pumping water from a well. What would happen if there were no sunlight for a week?
💬 Answer:
If there were no sunlight for a week —
1️⃣ The solar panels would not work, as they need sunlight to produce electricity. ⚡
2️⃣ The windmill may slow down, because wind movement depends partly on the Sun’s heat and air pressure changes. 💨
3️⃣ Plants would stop making food since they need sunlight for photosynthesis. 🌿
4️⃣ The weather would become cold and dark, and people would need to use artificial lights during the day. 💡
1️⃣ The solar panels would not work, as they need sunlight to produce electricity. ⚡
2️⃣ The windmill may slow down, because wind movement depends partly on the Sun’s heat and air pressure changes. 💨
3️⃣ Plants would stop making food since they need sunlight for photosynthesis. 🌿
4️⃣ The weather would become cold and dark, and people would need to use artificial lights during the day. 💡
💡 Conclusion: The Sun is the main source of energy on Earth — it helps generate light, wind, and even food energy for all living beings. 🌍☀️
💡 Did You Know?
Almost every form of energy — wind, solar, or food — can be traced back to the Sun! 🌞➡️💨➡️🌿➡️🔥
Q14.❓ Fill up the blanks using the following terms — (fossil fuels, forest, air, petroleum, coal, water and nonrenewable resource)
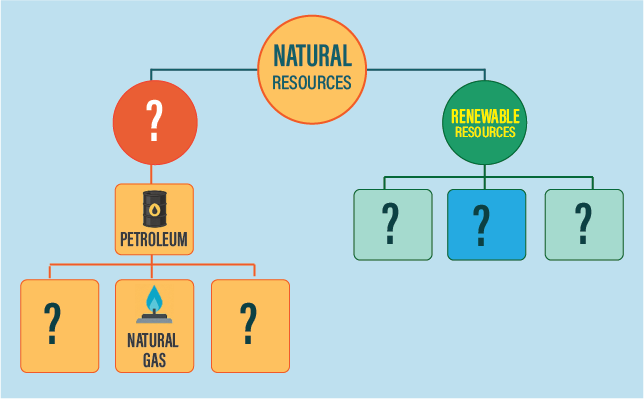
(Fill up the blanks with fossil fuels, forest, air, petroleum, coal, water and nonrenewable resource)
💬 Answer:
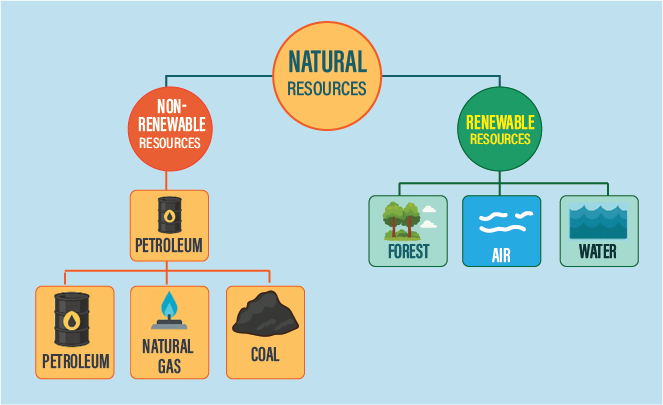
(Fossil fuels, forest, air, petroleum, coal, water and nonrenewable resource)
💡 Did You Know?
Fossil fuels like coal and petroleum are nonrenewable resources — once used, they take millions of years to form again.
🌲 Q.15. There is an increasing demand for trees to meet the requirements of industries and for housing.
Therefore, trees are being felled. Is it justified? Discuss and prepare a brief report. 🌍
💬 Answer:
🌿 Report on Tree Cutting and Its Effects
The cutting of trees to build houses or supply wood to industries is not justified if it is done without control or replantation.
Trees are essential for life — they give us oxygen, food, shelter, and rainfall, and help control pollution. 🌱
If trees are cut continuously:
1️⃣ The air becomes polluted as carbon dioxide increases. 🌫️
2️⃣ Soil erosion and floods occur due to loss of roots. 💧
3️⃣ Animals lose their homes, leading to loss of biodiversity. 🐿️
4️⃣ The climate becomes hotter and rainfall decreases. ☀️
However, if trees are cut responsibly, and new trees are planted in place of the old ones, it can be balanced. 🌳
The cutting of trees to build houses or supply wood to industries is not justified if it is done without control or replantation.
Trees are essential for life — they give us oxygen, food, shelter, and rainfall, and help control pollution. 🌱
If trees are cut continuously:
1️⃣ The air becomes polluted as carbon dioxide increases. 🌫️
2️⃣ Soil erosion and floods occur due to loss of roots. 💧
3️⃣ Animals lose their homes, leading to loss of biodiversity. 🐿️
4️⃣ The climate becomes hotter and rainfall decreases. ☀️
However, if trees are cut responsibly, and new trees are planted in place of the old ones, it can be balanced. 🌳
💡 Conclusion:
Tree cutting should be done only when necessary, and planting new trees must always follow.
Protecting trees means protecting life — for us and for future generations. 🌏💚
Tree cutting should be done only when necessary, and planting new trees must always follow.
Protecting trees means protecting life — for us and for future generations. 🌏💚
💡 Did You Know?
One big tree can supply oxygen for up to 10 people every day — imagine what a whole forest can do! 🌲🌲
💦 Q.16. Propose a plan to use less water in your school. What steps would you take to make this plan happen, and how would it help the environment? 🌍
💬 Answer:
🌱 My Water-Saving Plan for School
1️⃣ Check for Leaks: Regularly check and repair leaking taps, flushes, or pipes in classrooms and washrooms. 🚰
2️⃣ Use Buckets Instead of Running Taps: During cleaning, use buckets and mugs instead of leaving taps open. 🪣
3️⃣ Install Tap Timers: Fit automatic or push taps that stop water flow quickly to avoid wastage. ⏱️
4️⃣ Rainwater Harvesting: Set up a rainwater collection tank on the school roof to use for gardening and cleaning. 🌧️
5️⃣ Awareness Drive: Start a “Save Water Club” — make posters, perform skits, and spread awareness among students. 🎨📢
1️⃣ Check for Leaks: Regularly check and repair leaking taps, flushes, or pipes in classrooms and washrooms. 🚰
2️⃣ Use Buckets Instead of Running Taps: During cleaning, use buckets and mugs instead of leaving taps open. 🪣
3️⃣ Install Tap Timers: Fit automatic or push taps that stop water flow quickly to avoid wastage. ⏱️
4️⃣ Rainwater Harvesting: Set up a rainwater collection tank on the school roof to use for gardening and cleaning. 🌧️
5️⃣ Awareness Drive: Start a “Save Water Club” — make posters, perform skits, and spread awareness among students. 🎨📢
🌿 How it Helps the Environment:
• Saves freshwater for future generations. 💧
• Reduces energy use in pumping and purifying water. ⚡
• Helps plants and animals by keeping natural water sources full. 🐸🌾
• Teaches everyone to be responsible global citizens. 🌍
• Saves freshwater for future generations. 💧
• Reduces energy use in pumping and purifying water. ⚡
• Helps plants and animals by keeping natural water sources full. 🐸🌾
• Teaches everyone to be responsible global citizens. 🌍
💡 Did You Know?
If every student saves just 1 litre of water per day, an entire school can save thousands of litres every month! 💧🙌
📚 Explore More Class 6 Chapters (Questions and Answers)
🌍Chapter 1 – The Wonderful World of Science
🦁Chapter 2 – Diversity in the Living World
🥗Chapter 3 – Mindful Eating
🧲Chapter 4 – Exploring Magnets
📏Chapter 5 – Measurement of Length & Motion
🧱Chapter 6 – Materials Around Us
🌡️Chapter 7 – Temperature & Measurement
💧Chapter 8 – States of Water
⚗️Chapter 9 – Methods of Separation
🐾Chapter 10 – Living Creatures
🌿Chapter 11 – Nature's Treasures
🚀Chapter 12 – Beyond Earth
